VW Golf 7 Transmission Parts - Volkswagen Parts
Next >> VW tiguan engine parts
VW Golf 7 Transmission Parts List
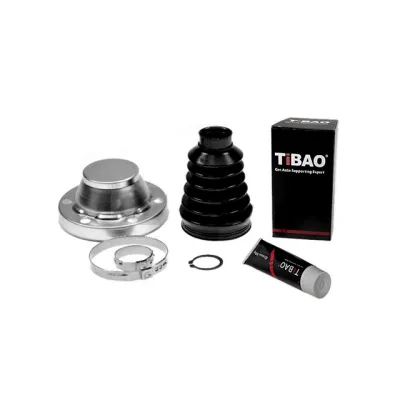

7L0498201A Transmission Parts C.V Joint Kit for AUDI TT, PORSCHE Cayenne, VW CARAVELLE, CUPRA LEON (KL1), SEAT LEON (5F1), SKODA FABIA II Combi (545), FABIA II Combi (5J, 545)
OE:
7L0 498 201 A
NID:
TW17C0413
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:7L0498201A Transmission Parts C.V Joint Kit for AUDI TT, PORSCHE Cayenne, VW CARAVELLE, CUPRA LEON (KL1), SEAT LEON (5F1), SKODA FABIA II Combi (545), FABIA II Combi (5J, 545)

1K0498201A Transmission Parts C.V Joint Kit for AUDI Q5, PORSCHE Cayenne, VW ARTEON, CUPRA LEON (KL1), SEAT LEON Hatchback Van (5F1), SKODA RAPID (NH3, NK3, NK6)
OE:
1K0 498 201 A
NID:
TW17C0484
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:1K0498201A Transmission Parts C.V Joint Kit for AUDI Q5, PORSCHE Cayenne, VW ARTEON, CUPRA LEON (KL1), SEAT LEON Hatchback Van (5F1), SKODA RAPID (NH3, NK3, NK6)

5Q0501117A Transmission Parts Wheel Hub Bearing for AUDI A3, VW GOLF, SEAT LEON ST (5F8), SKODA OCTAVIA III (5E3, NL3, NR3)
OE:
5Q0 501 117 A
NID:
TW17C0408
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:5Q0501117A Transmission Parts Wheel Hub Bearing for AUDI A3, VW GOLF, SEAT LEON ST (5F8), SKODA OCTAVIA III (5E3, NL3, NR3)

1KM498103 Transmission Parts CV Joint for VW PASSAT B8 Estate (3G5, CB5), GOLF VII (5G1, BQ1, BE1, BE2), BEETLE (9C1, 1C1), BORA IV (162, 163, AV3, AV2)
OE:
1KM 498 103
NID:
TW17C0383
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:1KM498103 Transmission Parts CV Joint for VW PASSAT B8 Estate (3G5, CB5), GOLF VII (5G1, BQ1, BE1, BE2), BEETLE (9C1, 1C1), BORA IV (162, 163, AV3, AV2)

5Q0199555T Transmission Parts Transmission Mount for AUDI A3, VW ARTEON, CUPRA FORMENTOR (KM7), SEAT LEON Hatchback Van (5F1), SKODA SUPERB III (3V3)
OE:
5Q0 199 555 T
NID:
TW17C0371
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:5Q0199555T Transmission Parts Transmission Mount for AUDI A3, VW ARTEON, CUPRA FORMENTOR (KM7), SEAT LEON Hatchback Van (5F1), SKODA SUPERB III (3V3)

113501229C Transmission Parts Bolt for AUDI A2, PORSCHE Cayenne, VW GOLF, SEAT TOLEDO IV (KG3)
OE:
113 501 229 C
NID:
ZW17C0172
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
中性/NEUTRAL
SPECS:
Matching Result:113501229C Transmission Parts Bolt for AUDI A2, PORSCHE Cayenne, VW GOLF, SEAT TOLEDO IV (KG3)

7H0498203 Transmission Parts C.V Joint Kit for AUDI Q2, PORSCHE Cayenne, VW PASSAT, CUPRA LEON (KL1), SEAT LEON (5F1), SKODA SUPERB III (3V3)
OE:
7H0 498 203
NID:
TW17C0103
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Fitting
Matching Result:7H0498203 Transmission Parts C.V Joint Kit for AUDI Q2, PORSCHE Cayenne, VW PASSAT, CUPRA LEON (KL1), SEAT LEON (5F1), SKODA SUPERB III (3V3)

357498103A Transmission Parts CV Joint for AUDI A1, VW POLO Vivo, SEAT LEON Hatchback Van (5F1), SKODA FABIA III (NJ3)
OE:
357 498 103 A
NID:
TW17C0039
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:357498103A Transmission Parts CV Joint for AUDI A1, VW POLO Vivo, SEAT LEON Hatchback Van (5F1), SKODA FABIA III (NJ3)

1K0498099E Transmission Parts C.V Joint for AUDI TT, VW BORA, CUPRA FORMENTOR (KM7), SEAT LEON (1P1), SKODA SUPERB III Estate (3V5)
OE:
1K0 498 099 E
NID:
TW17C0152
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
small
Matching Result:1K0498099E Transmission Parts C.V Joint for AUDI TT, VW BORA, CUPRA FORMENTOR (KM7), SEAT LEON (1P1), SKODA SUPERB III Estate (3V5)

1K0498203 Transmission Parts C.V Joint Kit for AUDI A3, VW POLO Vivo, SEAT IBIZA Mk V (KJ1, KJG), IBIZA V (KJ1, KJG), SKODA OCTAVIA III Combi (5E5, 5E6)
OE:
1K0 498 203
NID:
TW17C0284
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
small
Matching Result:1K0498203 Transmission Parts C.V Joint Kit for AUDI A3, VW POLO Vivo, SEAT IBIZA Mk V (KJ1, KJG), IBIZA V (KJ1, KJG), SKODA OCTAVIA III Combi (5E5, 5E6)

1K0498103A Transmission Parts CV Joint for AUDI Q3, VW CADDY, SEAT LEON (5F1), SKODA KODIAQ (NS7, NV7, NS6)
OE:
1K0 498 103 A
NID:
TW17C0251
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Manual
Matching Result:1K0498103A Transmission Parts CV Joint for AUDI Q3, VW CADDY, SEAT LEON (5F1), SKODA KODIAQ (NS7, NV7, NS6)

1K0498099G Transmission Parts C.V Joint for AUDI Q2, VW GOLF, SEAT LEON SC (5F5), SKODA KODIAQ (NS7, NV7, NS6)
OE:
1K0 498 099 G
NID:
TW17C0397
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:1K0498099G Transmission Parts C.V Joint for AUDI Q2, VW GOLF, SEAT LEON SC (5F5), SKODA KODIAQ (NS7, NV7, NS6)

1K0498201C Transmission Parts C.V Joint Kit for AUDI TT, VW GOLF, SEAT IBIZA III (6L1), IBIZA Mk III (6L1), SKODA SUPERB II Estate (3T5)
OE:
1K0 498 201 C
NID:
TW17C0172
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Automatic 69MM
Matching Result:1K0498201C Transmission Parts C.V Joint Kit for AUDI TT, VW GOLF, SEAT IBIZA III (6L1), IBIZA Mk III (6L1), SKODA SUPERB II Estate (3T5)

1K0498103C Transmission Parts CV Joint for AUDI A3, VW BORA, SEAT IBIZA Mk V (KJ1, KJG), IBIZA V (KJ1, KJG), SKODA OCTAVIA III Combi (5E5, 5E6)
OE:
1K0 498 103 C
NID:
TW17C0154
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:1K0498103C Transmission Parts CV Joint for AUDI A3, VW BORA, SEAT IBIZA Mk V (KJ1, KJG), IBIZA V (KJ1, KJG), SKODA OCTAVIA III Combi (5E5, 5E6)
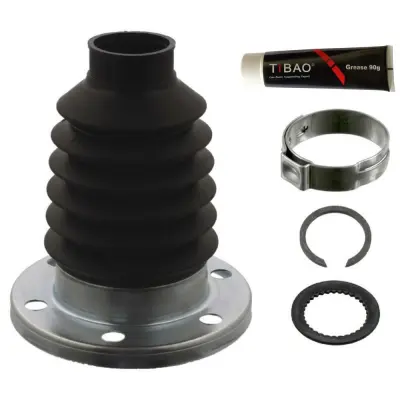

1K0498201B Transmission Parts C.V Joint Kit for AUDI A3, VW T-ROC, CUPRA FORMENTOR (KM7), SEAT LEON ST Estate Van (5F8), SKODA KAROQ (NU7, ND7)
OE:
1K0 498 201 B
NID:
TW17C0493
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:1K0498201B Transmission Parts C.V Joint Kit for AUDI A3, VW T-ROC, CUPRA FORMENTOR (KM7), SEAT LEON ST Estate Van (5F8), SKODA KAROQ (NU7, ND7)

1K0721261 Transmission Parts Clutch Slave Cylinder for AUDI Q2, VW SCIROCCO, SEAT LEON (1P1), SKODA KAROQ (NU7, ND7)
OE:
1K0 721 261
NID:
TW17C0156
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:1K0721261 Transmission Parts Clutch Slave Cylinder for AUDI Q2, VW SCIROCCO, SEAT LEON (1P1), SKODA KAROQ (NU7, ND7)

1K0498103C Transmission Parts CV Joint for AUDI A3, VW BORA, SEAT ARONA (KJ7, KJP), SKODA OCTAVIA III Combi (5E5, 5E6)
OE:
1K0 498 103 C
NID:
TW17C0323
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:1K0498103C Transmission Parts CV Joint for AUDI A3, VW BORA, SEAT ARONA (KJ7, KJP), SKODA OCTAVIA III Combi (5E5, 5E6)

5N0711761 Transmission Parts Gear Cable End for AUDI TT, VW T-ROC, SEAT TOLEDO IV (KG3), SKODA FABIA II (542), FABIA II (5J, 542)
OE:
5N0 711 761
NID:
TW17C0447
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:5N0711761 Transmission Parts Gear Cable End for AUDI TT, VW T-ROC, SEAT TOLEDO IV (KG3), SKODA FABIA II (542), FABIA II (5J, 542)

02E325201D Engine Parts Transmission Oil Sump for AUDI A3, VW EOS, SEAT LEON ST (5F8), SKODA SUPERB II (3T4)
OE:
02E 325 201D
NID:
ZW27C0063
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
中性/NEUTRAL
SPECS:
side
Matching Result:02E325201D Engine Parts Transmission Oil Sump for AUDI A3, VW EOS, SEAT LEON ST (5F8), SKODA SUPERB II (3T4)

1K0498099B Transmission Parts C.V Joint for AUDI TT, VW CC, SEAT LEON (1P1), SKODA LAURA II (1Z3), OCTAVIA II (1Z3)
OE:
1K0 498 099 B
NID:
TW17C0153
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Big
Matching Result:1K0498099B Transmission Parts C.V Joint for AUDI TT, VW CC, SEAT LEON (1P1), SKODA LAURA II (1Z3), OCTAVIA II (1Z3)

191498201D Transmission Parts C.V Joint Kit for AUDI A3, VW GOLF, SKODA SUPERB III (3V3)
OE:
191 498 201D
NID:
ZW17C0116
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
中性/NEUTRAL
SPECS:
Matching Result:191498201D Transmission Parts C.V Joint Kit for AUDI A3, VW GOLF, SKODA SUPERB III (3V3)

5K0711203B Transmission Parts Shift Joint for AUDI TT, VW CADDY, SEAT LEON (1P1), SKODA SUPERB III (3V3)
OE:
5K0 711 203 B
NID:
TW17C0412
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:5K0711203B Transmission Parts Shift Joint for AUDI TT, VW CADDY, SEAT LEON (1P1), SKODA SUPERB III (3V3)

5M0498099 Transmission Parts C.V Joint for AUDI A3, VW T-ROC, SEAT LEON (1P1), SKODA OCTAVIA II Combi (1Z5)
OE:
5M0 498 099
NID:
TW17C0301
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:5M0498099 Transmission Parts C.V Joint for AUDI A3, VW T-ROC, SEAT LEON (1P1), SKODA OCTAVIA II Combi (1Z5)
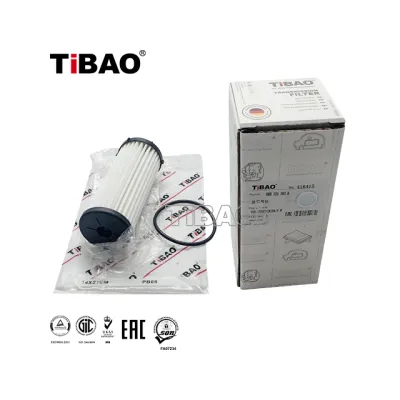

0BH325183B Transmission Parts Gearbox Filter Element for AUDI A3, VW GOLF, SEAT ALHAMBRA (710, 711), SKODA KODIAQ (NS7, NV7, NS6)
OE:
0BH 325 183 B
NID:
HA17C0014
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO HD
SPECS:
Matching Result:0BH325183B Transmission Parts Gearbox Filter Element for AUDI A3, VW GOLF, SEAT ALHAMBRA (710, 711), SKODA KODIAQ (NS7, NV7, NS6)

02E305051C Transmission Parts Gearbox Oil Grid for AUDI Q3, VW SHARAN, SEAT ATECA (KH7, KHP), SKODA LAURA II (1Z3), OCTAVIA II (1Z3)
OE:
02E 305 051 C
NID:
TW17C0337
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:02E305051C Transmission Parts Gearbox Oil Grid for AUDI Q3, VW SHARAN, SEAT ATECA (KH7, KHP), SKODA LAURA II (1Z3), OCTAVIA II (1Z3)

5Q0721388G Transmission Parts Clutch Master Cylinder for AUDI A3, VW ARTEON, CUPRA FORMENTOR (KM7), SEAT LEON ST (5F8), SKODA SUPERB III (3V3)
OE:
5Q0 721 388 G
NID:
TW17C0392
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:5Q0721388G Transmission Parts Clutch Master Cylinder for AUDI A3, VW ARTEON, CUPRA FORMENTOR (KM7), SEAT LEON ST (5F8), SKODA SUPERB III (3V3)

5Q0199855Q Transmission Parts Transmission Mount for AUDI TT, VW GOLF, SEAT LEON SC (5F5), SKODA OCTAVIA III Combi (5E5, 5E6)
OE:
5Q0 199 855 Q
NID:
TW17C0395
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:5Q0199855Q Transmission Parts Transmission Mount for AUDI TT, VW GOLF, SEAT LEON SC (5F5), SKODA OCTAVIA III Combi (5E5, 5E6)

5K0711203A Transmission Parts Shift Joint for AUDI A3, VW MAGOTAN, SEAT ALTEA (5P1), SKODA SUPERB II (3T4)
OE:
5K0 711 203 A
NID:
TW17C0444
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:5K0711203A Transmission Parts Shift Joint for AUDI A3, VW MAGOTAN, SEAT ALTEA (5P1), SKODA SUPERB II (3T4)
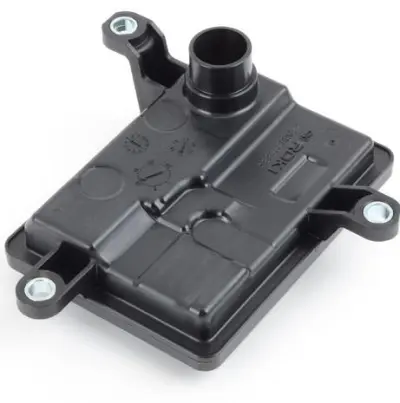

09G325429E Transmission Parts A/T Filter for VW POLO, SEAT IBIZA Mk V (KJ1, KJG), IBIZA V (KJ1, KJG), SKODA RAPID (NA2)
OE:
09G 325 429 E
NID:
TW17C0353
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:09G325429E Transmission Parts A/T Filter for VW POLO, SEAT IBIZA Mk V (KJ1, KJG), IBIZA V (KJ1, KJG), SKODA RAPID (NA2)

1K0407272RG Transmission Parts Driveshaft for AUDI A3, VW MAGOTAN, SEAT LEON SC (5F5), SKODA OCTAVIA III (5E3, NL3, NR3)
OE:
1K0 407 272 RG
NID:
TW17C0403
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:1K0407272RG Transmission Parts Driveshaft for AUDI A3, VW MAGOTAN, SEAT LEON SC (5F5), SKODA OCTAVIA III (5E3, NL3, NR3)

6Q0721261D Transmission Parts Clutch Slave Cylinder for AUDI A3, VW POLO, BUICK (SGM) REGAL II (EG1), SEAT LEON (5F1), SKODA YETI (5L)
OE:
6Q0 721 261 D
NID:
TW17C0162
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Matching Result:6Q0721261D Transmission Parts Clutch Slave Cylinder for AUDI A3, VW POLO, BUICK (SGM) REGAL II (EG1), SEAT LEON (5F1), SKODA YETI (5L)

6Q0721261A Transmission Parts Clutch Slave Cylinder for AUDI A3, VW GOLF, BUICK (SGM) REGAL II (EG1), SEAT LEON (5F1), SKODA YETI (5L)
OE:
6Q0 721 261 A
NID:
ZW17C0058
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
中性/NEUTRAL
SPECS:
Matching Result:6Q0721261A Transmission Parts Clutch Slave Cylinder for AUDI A3, VW GOLF, BUICK (SGM) REGAL II (EG1), SEAT LEON (5F1), SKODA YETI (5L)

1K0407271BD Transmission Parts Driveshaft for AUDI A3, VW BORA, SKODA YETI (5L)
OE:
1K0 407 271BD
NID:
TW17C0237
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Front L
Matching Result:1K0407271BD Transmission Parts Driveshaft for AUDI A3, VW BORA, SKODA YETI (5L)

1K0407272FS Transmission Parts Driveshaft for AUDI A3, VW CC, SEAT ALTEA XL (5P5, 5P8), SKODA OCTAVIA III (5E3, NL3, NR3)
OE:
1K0 407 272 FS
NID:
TW17C0304
MOQ:
50
BRAND:
TiBAO
SPECS:
Front R
Matching Result:1K0407272FS Transmission Parts Driveshaft for AUDI A3, VW CC, SEAT ALTEA XL (5P5, 5P8), SKODA OCTAVIA III (5E3, NL3, NR3)