BMW F10 Engine Parts - 5 Series Aftermarket Parts
|
The BMW F10, which is the sixth generation of the BMW 5 Series, offers a range of engine options. Below is a detailed breakdown of key engine parts typically found in the BMW F10: Engine Block: Cylinder Head: Made of aluminum alloy, it contains the combustion chambers and valves, supporting camshafts that control the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves. Pistons and Connecting Rods: The pistons, made from lightweight, heat-resistant alloys, move up and down within the cylinders, converting fuel combustion into mechanical motion. Connecting rods link the pistons to the crankshaft, converting linear piston motion into rotational crankshaft movement. Crankshaft: Typically made from forged steel, the crankshaft converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational energy that drives the wheels. Valvetrain (Camshafts, Valves, and Lifters): The camshafts control the timing of the intake and exhaust valves. The valves regulate air-fuel intake and exhaust output, while the lifters transfer camshaft motion to the valves. Turbocharger (if equipped): Compresses air entering the engine for a denser air-fuel mixture, increasing power output. Turbochargers are common in models like the BMW 535i, made of heat-resistant materials. Fuel Injection System: Direct injection delivers fuel directly into the combustion chamber, optimizing efficiency. Injectors control fuel amount and timing, while the fuel pump ensures high-pressure fuel delivery to the injectors. Cooling System: The radiator cools the engine by transferring heat from the coolant to the air. The water pump circulates coolant through the engine, and the thermostat regulates the coolant flow to maintain proper engine temperature. Oil System: The oil pump lubricates engine components by circulating oil, with the oil pan storing it and the oil filter removing contaminants to protect the engine. Intake and Exhaust Manifolds: The intake manifold distributes the air-fuel mixture to each cylinder, while the exhaust manifold collects exhaust gases and directs them to the exhaust system. Electronic Control Unit (ECU): The ECU manages key engine functions like air-fuel ratio, ignition timing, and emissions control for optimal performance and efficiency. Exhaust System: The catalytic converter reduces harmful emissions, and the muffler decreases exhaust noise. Timing Chain or Belt: Synchronizes the crankshaft and camshaft rotations to ensure precise valve timing during intake and exhaust strokes. Each of these components works in harmony to ensure the BMW F10 engine operates efficiently and delivers the high performance expected from a BMW. Different F10 models, such as the 520i, 535i, or M5, may have variations in these components, especially between turbocharged and naturally aspirated engines. |
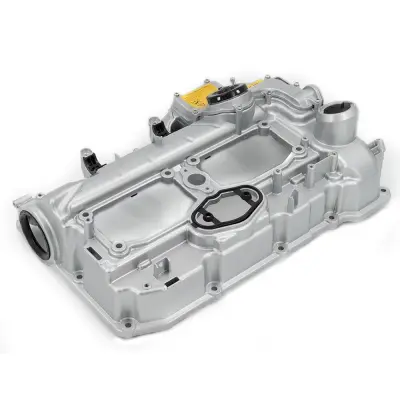






















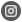


 Most F10 engines have an aluminum engine block for reduced weight and improved performance. It houses key components like the cylinders, pistons, and crankshaft, forming the foundation of the engine.
Most F10 engines have an aluminum engine block for reduced weight and improved performance. It houses key components like the cylinders, pistons, and crankshaft, forming the foundation of the engine.